|
Install Django
2016/06/13 |
|
Install Django which is Python Web Application Framework.
|
|
| [1] | Install some packages. |
|
root@www:~# apt-get -y install python-virtualenv
|
| [2] | Install Django under a Virtualenv environment. It's possible to do for any common user. |
|
ubuntu@www:~$ virtualenv venv ubuntu@www:~$ cd ~/venv ubuntu@www:~/venv$ source bin/activate (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv$ pip install -U pip (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv$ pip install django
Collecting django
Downloading Django-1.9.7-py2.py3-none-any.whl (6.6MB)
100% |##############################| 6.6MB 222kB/s
Installing collected packages: django
Successfully installed django-1.9.7
(venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv$
django-admin --version 1.9.7 # exit from virtualenv (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv$ deactivate ubuntu@www:~/venv$ |
| [3] | Create a test project. |
|
# create "testproject" (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv$ django-admin startproject testproject (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv$ cd testproject # configure database (default is SQLite) (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$ python manage.py migrate
# create admin user (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$ python manage.py createsuperuser Username (leave blank to use 'ubuntu'): ubuntu Email address: ubuntu@www.srv.world Password: Password (again): Superuser created successfully. # start server venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$ python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 Performing system checks... System check identified no issues (0 silenced). June 15, 2016 - 00:30:06 Django version 1.9.7, using settings 'testproject.settings' Starting development server at http://0.0.0.0:8000/ Quit the server with CONTROL-C. |
| [4] | Access to the "http://(server's hostname or IP address):8000/" from a client computer. It's OK if following site is displayed normally. |
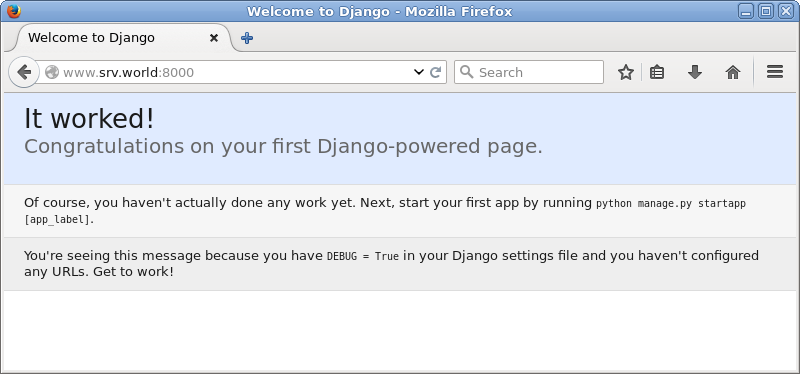
|
| [5] | It's possible to user admin site on "http://(server's hostname or IP address):8000/admin". |
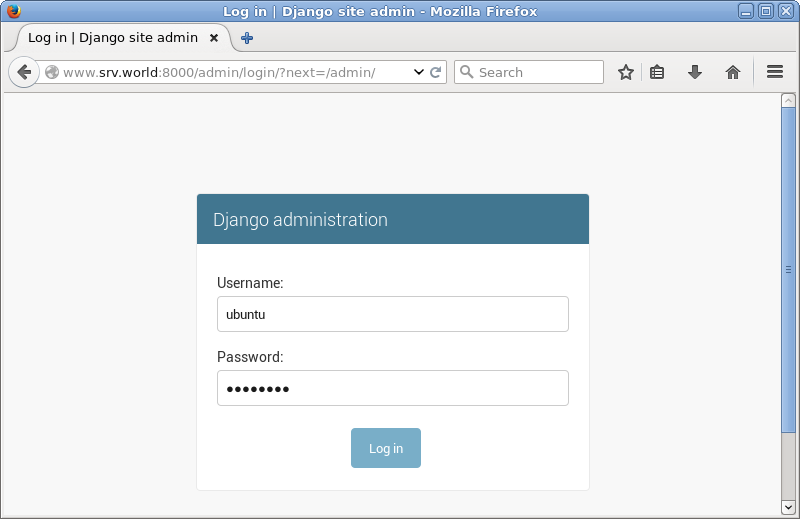
|

|
| [6] | Create a test application. |
|
ubuntu@www:~$
(venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$ cd ~/venv ubuntu@www:~/venv$ source bin/activate (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv$ cd testproject python manage.py startapp testapp
(venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$
vi testapp/views.py # add to the end
from django.http import HttpResponse
def main(request):
html = '<html>\n' \
'<body>\n' \
'<div style="width: 100%; font-size: 40px; font-weight: bold; text-align: center;">\n' \
'Django Test Page\n' \
'</div>\n' \
'</body>\n' \
'</html>\n'
return HttpResponse(html)
(venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$
mv testproject/urls.py testproject/urls.py.org (venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$ vi testproject/urls.py # create new
from django.conf.urls import patterns, url
urlpatterns = patterns('',
url(r'^testapp/$', 'testapp.views.main'),
)
(venv)ubuntu@www:~/venv/testproject$
vi testproject/settings.py # add testapp like follows
INSTALLED_APPS = (
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'testapp',
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 |
| [7] | Access to the "http://(server's hostname or IP address):8000/testapp/" from a client computer. It's OK if testapp is displayed normally. |

|